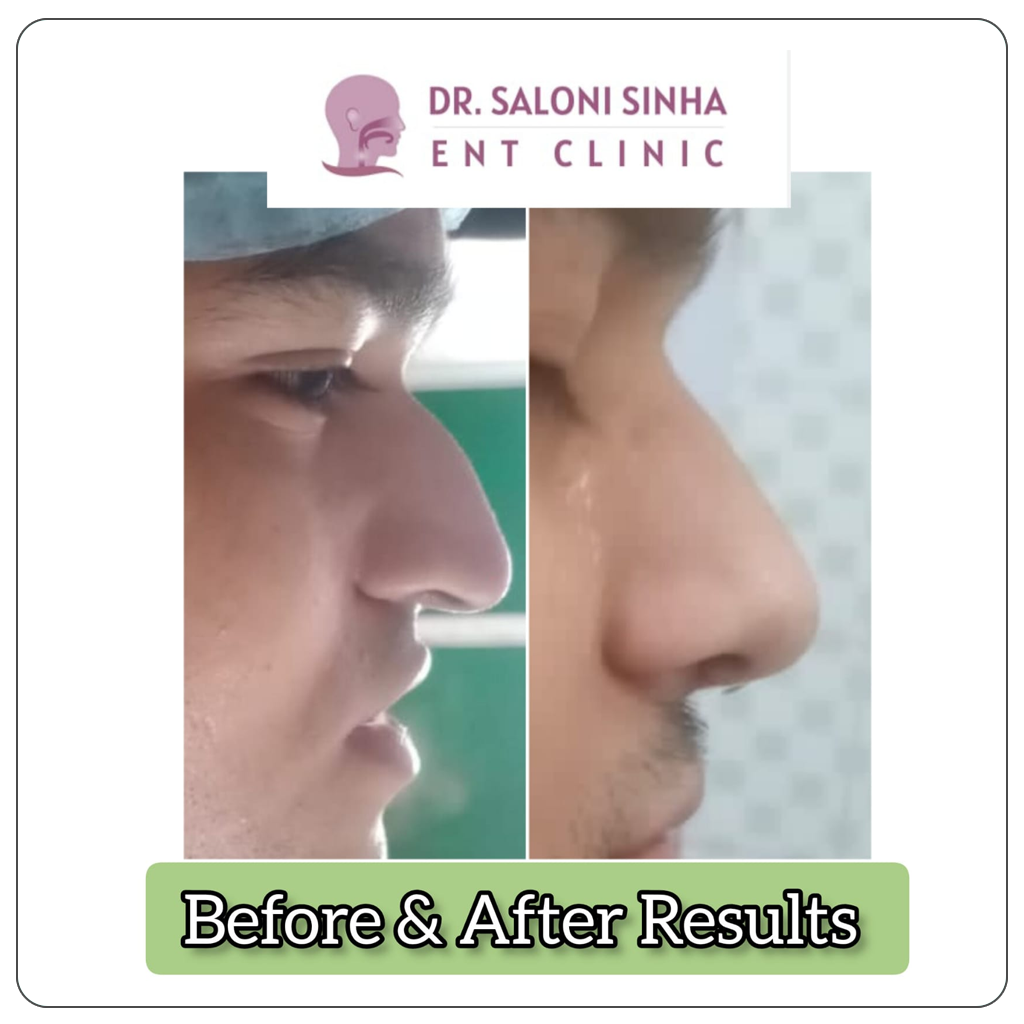
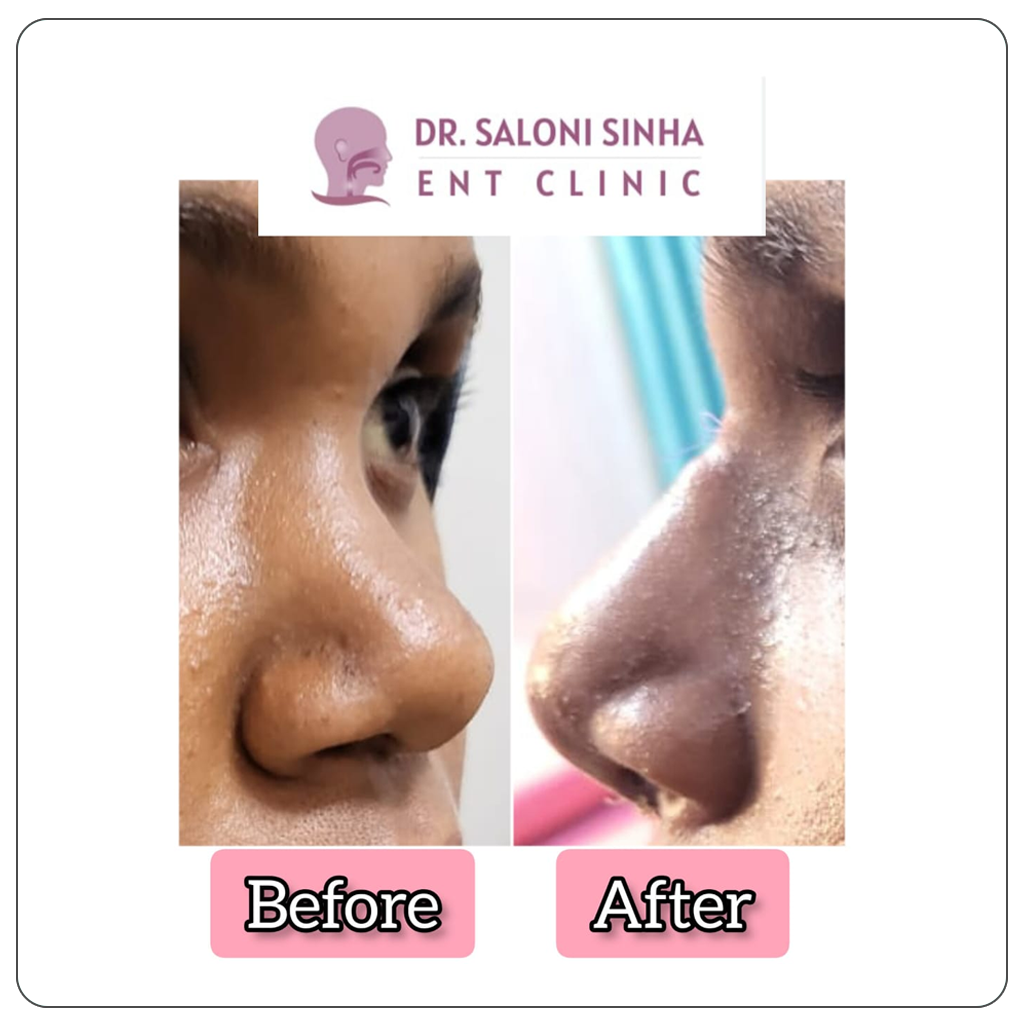
Best Thyroid and Parotid Gland Treatment at Affordable Cost
The oral cavity houses two types of salivary glands. One type is the minor salivary glands that line up the mucosal layer and are present in plenty, overwhelming the entire mouth. The second type is the major salivary glands, namely:
- • Parotid- situated deep within the cheek
- • Submandibular- Present under the edge of each jaw
- • Sublingual- Below the tongue
The throat has one of the major thyroid hormone-producing gland, the thyroid gland, which is a butterfly-shaped gland, contributing to various functions ranging from temperature regulation to metabolism regulation in the body.
Both thyroid and parotid glands are important glands of the oral and throat regions. When there is a blockage, damage, or abnormal growths pertaining to these glands, surgery to eliminate the damage is essential.
While blockage of the parotid gland restricts the outflow of saliva that can lead to salivary gland enlargement. Similarly, a damaged or non-functional thyroid can lead to abnormal thyroid values, metabolic issues, and hormonal imbalances. According to the condition and precise diagnosis, a neck mass surgery pertaining to the salivary glands and thyroid is performed to enable smooth functioning.
Thyroid Surgery or Thyroidectomy
Thyroidectomy is the surgical removal of all or part of the thyroid gland. This surgery helps treat thyroid disorders, cancerous and noncancerous growths of the thyroid (goitre), an overactive thyroid, or hyperthyroidism. Partial thyroidectomy involves the removal of a portion or part of the thyroid, and total thyroidectomy involves the whole thyroid removal. The type of thyroidectomy performed depends on the reason for the surgery.
Why is Thyroidectomy Performed?
Thyroidectomy may be recommended or required for one of the following reasons:
- • Thyroid cancer: Thyroidectomy of a part or all of the thyroid gland, depending on the condition, is a possible treatment option for thyroid cancers.
- • Goitre or Noncancerous enlargement of the thyroid: Large goitre or thyroid enlargement can cause swallowing and breathing issues with hyperthyroidism (excess thyroid hormone production or overactive thyroid).
- • Overactive thyroid or hyperthyroidism: Excess thyroxine production is one of the primary indications of hyperthyroidism. When medications or iodine therapy are not enough or cannot be used thyroidectomy is an alternative treatment option.
Intermediate thyroid nodules: Thyroid nodules can be benign or malignant and need to be removed through thyroidectomy.
How is Thyroidectomy Performed?
The thyroid removal surgery is usually performed under anaesthesia. After anaesthesia administration, the surgeon takes you through the following steps of thyroidectomy.
- • The surgeon makes a small incision in the lower centre of your neck and is done by one of the following methods.
- • Conventional thyroidectomy: The incision is made in the centre of the neck where the thyroid is directly accessed and removed according to the condition.
- • Transoral thyroidectomy: This method does not involve a neck incision, instead the thyroid is accessed through the mouth.
- • Endoscopic thyroidectomy: In this method, a very small incision in the neck allows surgical instruments and an endoscope (device embedded with light and camera source). The surgery is guided by an endoscope.
Aftercare and Recovery of Thyroidectomy
The thyroidectomy surgery may take at least two to three hours. After surgery, you will be monitored for some time and later be shifted to the ward. Sometimes, a drain pipe may be placed, at the incision that will be removed a day after surgery. After a thyroidectomy, you may experience pain in the neck and hoarse or weak voices that are temporary and normalised over time. You can eat and drink as usual post-surgery and will be permitted to go home after a day or two. If an incision is made during the surgery, it may take up to a year for the scar to fade. Check with your doctor about which over-the-counter creams to reduce scars are safe to use. You will need to refrain from vigorous activities for a couple of weeks post thyroidectomy.